Data 2010 en
Data of the Consulting Laboratory for Haemophilus influenzae 2010
Introduction
The Consulting Laboratory for Haemophilus influenzae (KLHi) has been assigned the laboratory surveillance of invasive H. influenzae infections in Germany by the Robert Koch Institute (RKI). Its tasks include serotyping of clinical isolates and antibiotic resistance surveillance. In 2010, samples from 162 patients were analysed. In 143 patients, H. influenzae was isolated from primarily sterile samples (this figure equals the number of invasive diseases).
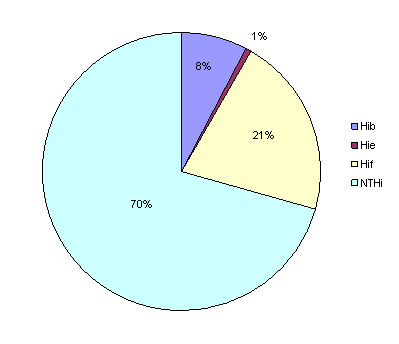
The vast majority of these invasive cases were infected by non-typeable H. influenzae (NTHi, 101 cases, 70.6 %), followed by Hif as the most frequent capsular serotype (30 cases; 21.0 %). Hib showed third highest frequency among the serotypes (11 cases; 7.7 %), and only one case of Hie (0.7 %) was detected. Other serotypes were not found.
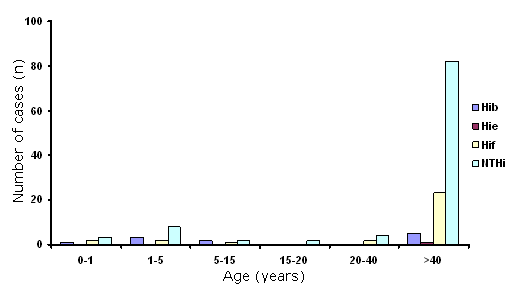
As in previous years (e.g. 2008, cf. Robert Koch Institute, Epidemiologisches Bulletin 35/2009) the age group most affected by invasive H. influenzae disease is > 40 years (111 cases, 77.2 %).
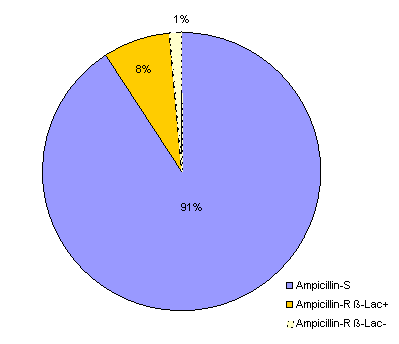
The KLHi recently started analyzing retrospectively the frequency of ampicillin resistance of invasive isolates. In 2010, ampicillin resistance was found in 13 clinical isolates (10%), of which 11 showed β lactamase production. Thus, two isolates are considered as BLNAR (β-lactamase negative ampicillin resistant) H. influenzae.
In 2010, 210 cases have been registered in the statutory notification system as recorded on SurvStat@RKI. Laboratory surveillance, therefore, likely covers about 70% of the cases. This estimation is in accordance with a matching performed with notification data from Baden-Württemberg showing a coverage of about 80%.
Serotype distribution of invasive H. influenzae isolates in 2010
Age distribution of patients with invasive H. influenzae disease
Serotype distribution in Federal States
| BW | BY | BE | BB | HB | HH | HE | MV | NI | NW | RP | SL | SN | ST | SH | TH |
Hib | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
Hie | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Hif | 5 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 2 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
NTHi | 20 | 16 | 9 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 10 | 25 | 4 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
BW: Baden-Württemberg, BY: Bavaria, BE: Berlin, BB: Brandenburg, HB: Bremen, HH: Hamburg, HE: Hessen, MV: Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, NI: Lower Saxony, NW: North Rhine-Westphalia, RP: Rhineland-Palatinate, SL: Saarland, SN: Saxony, ST: Saxony-Anhalt, SH: Schleswig-Holstein, TH: Thuringia. The table comprises a total of 143 cases.
Ampicillin resistance in invasive H. influenzae isolates
Publications of the KLHi
Articles:
- Lâm TT, Elias J, Frosch M, Vogel U, Claus H. New diagnostic PCR for Haemophilus influenzae serotype e based on the cap locus of strain ATCC 8142. Int J Med Microbiol. 2011 Feb;301(2):176-9.
- Lâm TT, Frosch M, Claus H, Vogel U. Sequence analysis of the serotype-specific synthesis regions II of Haemophilus influenzae serotypes c and d: evidence for common ancestry of capsule synthesis in Pasteurellaceae and Neisseria meningitidis. Research in Microbiology 2011 (in press).
Book chapters:
- Vogel U et al. (2010) MiQ 13a und 13b: Infektionen des Mundes und der oberen Atemwege. In: A. Podbielski, M. Herrmann, E. Kniehl, H. Mauch and H. Rüssmann (Hrg.). Mikrobiologisch-infektiologische Qualitätsstandards (MIQ), 2. Auflage. München: Urban und Schwarzenberg (Elsevier).
Disclaimer: the above data were generated with federal funds (RKI). Scientific use is prohibited without prior written consent by KLHi or RKI. Commercial use is strictly prohibited. Inclusion of figures or tables in talks or oral presentations is not allowed.