Daten 2016 en
Data of the NRZMHi for Haemophilus influenzae 2016
1. Introduction
The tasks of the National Reference Laboratory for Meningococci and Haemophilus influenzae (NRZMHi) assigned by the Robert Koch Institute for the surveillance of invasive Haemophilus influenzae disease include serotyping of clinical isolates from blood or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and the detection of antibiotic resistance against ß-lactam antibiotics.
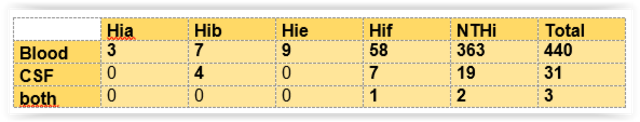
In 2016, all in all 570 submissions were analyzed including bacterial isolates from 488 patients with invasive infections. The NRZMHi could confirm the diagnosis Haemophilus influenzae in 474 cases. Among these isolates, 440 derived from blood, 31 from cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) only. We received H. influenzae found in blood as well as CSF from three patients. Detection of H. influenzae from these materials must be notified according to the German Infection Protection Act (IfSG). Seven strains were H. parainfluenzae. In further seven cases, no H. influenzae was cultivated from the submitted material.
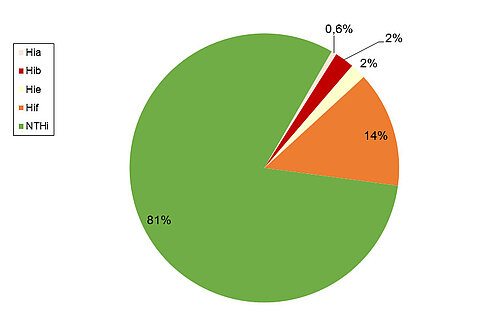
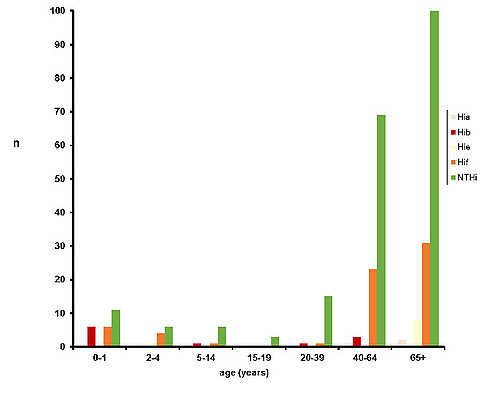
As in previous years, the majority of blood or CSF isolates were non-typeable H. influenzae (NTHi, 385 isolates, 81.2 %), followed by Hif as the most frequent capsular serotype (66 cases; 13.9 %). However, Hib showed third highest frequency among the serotypes (11 cases; 2.3 %), surpassing the prevalence of Hie (9 cases; 1.9%), which was more frequent in previous years. Of the rare serotypes, three Hia, and no Hic or Hid were isolated. Among the analyzed cases, the age group most affected was > 40 years (412 cases; 86.9 % of all cases). In addition, a significant percentage of cases (34 cases; 7.2 %) was found in children aged <5 years.
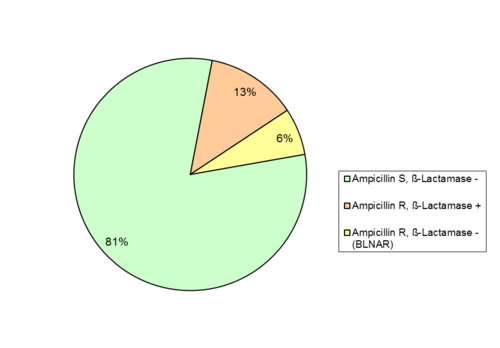
The NRZMHi analyzed the frequency of ampicillin resistance using gradient agar diffusion tests (E-test). Ninety-one isolates (19.2 %) were ampicillin resistant (MIC > 1 µg/ml), of which 60 (65.9 %) showed β‑lactamase production.
2. Serotype distribution of H. influenzae isolates from blood or CSF in 2016
3. Age distribution of patients with H. influenzae detected in blood or CSF
4. Serotype distribution in Federal States
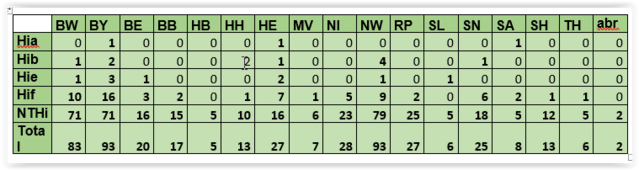
BW: Baden-Württemberg, BY: Bavaria, BE: Berlin, BB: Brandenburg, HB: Bremen, HH: Hamburg, HE: Hesse, MV: Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, NI: Lower Saxony, NW: North Rhine-Westfalia, RP: Rhineland-Palatinate, SL: Saarland, SN: Saxony, ST: Saxony-Anhalt, SH: Schleswig-Holstein, TH: Thuringia, abr: abroad.
In one case, the origin of the isolate was not indicated.
5. Serotype distribution according to site of isolation
6. Ampicillin resistance in isolates H. influenzae from blood or CSF
7. Publications of the NRZMHi on Haemophilus influenzae:
Original Articles
- Lâm TT, Elias J, Frosch M, Vogel U, Claus H. New diagnostic PCR for Haemophilus influenzae serotype e based on the cap locus of strain ATCC 8142. Int J Med Microbiol. 2011 Feb;301(2):176-9.
- Lâm TT, Frosch M, Claus H, Vogel U. Sequence analysis of the serotype-specific synthesis regions II of Haemophilus influenzae serotypes c and d: evidence for common ancestry of capsule synthesis in Pasteurellaceae and Neisseria meningitidis. Research in Microbiology 2011 Jun;162(5):483-7.
- Lâm, T.T., Claus, H., Elias, J., Frosch, M., Vogel, U., 2015b. Ampicillin resistance of invasive Haemophilus influenzae isolates in Germany 2009-2012.Int J Med Microbiol. 2015 Oct;305(7):748-55.
- Lâm, T.T., Claus, H., Frosch, M., Vogel, U., 2016. Analysis of non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae in invasive disease reveals lack of the capsule locus. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2016 Jan;22(1):63.e7-8
Reviews
- Lâm TT, Claus H, Elias J, Hellenbrand W, Imöhl M, Prelog M, Sing A, van der Linden M, Vogel U. Infections with Pneumococci, Menigococci, H. influenzae and Diphtheria in Germany: the RKI Reference Network for Invasive Bacterial Infections (IBI) at the 5th Würzburg Workshop on Epidemiology, Prevention and Therapy for Invasive Meningococcal Diseases 2010 (Meeting Report). Gesundheitswesen. 2011. DOI: 10.1055/s-0031-1286269.
Disclaimer: the above data were generated with federal funds (RKI). Scientific use is prohibited without prior written consent by KLHi or RKI. Commercial use is strictly prohibited. Inclusion of figures or tables in talks or oral presentations is not allowed.